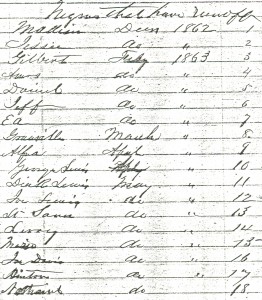Posts Tagged ‘Civil War’
Tuesday, November 24th, 2009

In 1847 an enslaved African American, Dred Scott, went to trial to sue for his freedom. This case, which later became known as Dred Scott v. Sanford, impacted the citizenship of all African Americans throughout the United States.
Dred Scott was born a slave in Southampton County, Virginia and was owned by Peter Blow. Peter Blow was the great-nephew of Colonel Michael Blow who owned my ancestors before they were brought to Wessyngton Plantation by Joseph Washington.
Scott was taken to Alabama by the Blow family and later to St. Louis. After Peter Blow’s death in 1832, Scott was bought by an army surgeon Dr. John Emerson who took him to Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory.
Scott’s stay in Illinois and Wisconsin, where slavery was prohibited, gave him the legal standing to make a claim for his freedom. The abolitionists encouraged him to sue for his freedom. The case and appeals took ten years. In March 1857, the United States Supreme Court declared that all blacks, slaves as well as free blacks, were not, and could never become, citizens of the United States.
The decision was a victory for southern slaveholders, while northerners were outraged at its outcome. The Dred Scott case influenced the nomination of Abraham Lincoln to the Republican Party and his election that led to the South’s secession from the Union and ultimately the freedom of all African Americans.
Peter Blow’s sons, who had grown up with Dred Scott, helped him pay the legal fees for his lengthy case. After the Supreme Court’s decision, they purchased Scott and his wife and then emancipated them.
Dred Scott died nine months later—a free man.
.
Tags:Abraham Lincoln, Blow Family, Civil War, Confederate States, Declaration of Independence, Dr. John Emerson, Dred Scott, Dred Scott Decision, Frederick Douglass, Free Territory, Joseph Washington, Michael Blow, Missouri Compromise, Peter Blow, Runaway Slave Law, Scott vs. Sanford, Slave Laws, Southampton County Virginia, St. Louis, Supreme Court, Union Army
Posted in Civil War, Current Events, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Monday, November 2nd, 2009

Archaeological Dig at Wessyngton Slave Cabin Site
In 1991, I had an opportunity that few historians or genealogists ever have; to literally walk in your ancestors’ footsteps. In 1989 I was approached by the president of the Bloomington-Normal black history Project and director of the Midwestern archaeological research Center, about the potential investigations of the salve cabin area on Wessyngton Plantation to get an interpretation of slave life there. Similar digs have been conducted at the Hermitage, Mt. Vernon, and Monticello.
The actual digging at Wessyngton did not start until 1991. The thought of actually walking in my ancestors’ footsteps and holding objects they used in their everyday lives one hundred years earlier was surreal to me. Three sections of the slave cabin area were selected for exploration. One site was where the cabin of my great-great-grandparents Emanuel and Henny Washington once stood.
The dig yielded fragments of pottery and dishes used by my ancestors as well as coins and arrowheads made by Native Americans.
The photograph above shows the site of the archaeological dig on Wessyngton Plantation where my ancestors once lived.
Tags:African American History, African Slavery, Arrowheads, black history, Black History Month, Civil War, Monticello, Mt. Vernon, Native Americans, Plantation Archaeology, plantation slavery, Slave Cabin, Slave Housing, Slave Life, Tennessee slavery, The Hermitage
Posted in Civil War, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Sunday, October 18th, 2009

Joseph Washington 1895-2002
In more than thirty years of researching my ancestry and the lives of African Americans enslaved on Wessyngton Plantation, I have had the honor of interviewing more than twenty individuals whose parents or grandparents lived on the plantation. These individuals ranged in age from eighty to 107 years old.
Although I found hundreds of documents about my ancestors from plantation records written by the owners of Wessyngton, I learned many personal things about my ancestors from conducting interviews with elder family members.
In 1994, I visited my cousin Joseph Washington 1895-2002 (pictured above) at his home in Mansfield, Ohio on his one hundred second birthday. As a child Joseph lived next door to my great-great-grandparents Emanuel and Henny Washington who were born at Wessyngton in the early 1800s. He related many stories about them to me including ghost stories that my great-great-grandfather used to tell all the children on the plantation and songs he used to sing. Joseph told me what life was like on the plantation when he grew up there and how many people on the plantation were related to one another.
Oral history is a vital key to tracing African American genealogy and provides many details about our ancestors that can’t be found in records.
Tags:African American History, African American Oral History, African American slavery, Black Genealogy, black history, Civil War, family history, Griot, Interviews, Joseph Washington, Oral History, Oral Tradition, plantation slavery, Plantations, Tennessee history, Tennessee slavery
Posted in Civil War, Current Events, Interviews, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Wednesday, October 14th, 2009
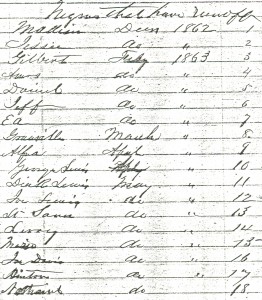
Runaway Slaves from Wessyngton Plantation 1862-1863
President Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation, issued September 22, 1862, declared freedom to slaves in the confederate states that did not return to the control of the Union by January 1, 1863. It did not free slaves from the border states Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri, and Tennessee. Many slaves from these states, however, were already free by this time due to self-emancipation─running away or being abandoned by their owners.
George A. Washington realized that his slaves would soon be tempted to leave his plantation Wessyngton. At the same time the Union Army was recruiting black soldiers, George made an offer to hire some of his slaves for a rate of $10 per month. From February through May 1863, twenty-four men agreed to stay on the plantation and work for the offered $10 per month. Of those twenty-four, however; eighteen left within a few months. The men had worked on the plantation all their lives and no doubt wanted to see what the outside world had to offer and to taste freedom. The men must have seen the offered salary as an attempt to keep them on the plantation. The above document lists the eighteen individuals who ran away from Wessyngton Plantation from 1862-1863.
Tags:Abraham Lincoln, Civil War, Confederate Army, Contraband, Contraband Camps, Emancipation, Emancipation Proclamation, plantation slavery, President Lincoln, runaway slaves, Union Army
Posted in Civil War, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Wednesday, October 7th, 2009

Wessyngton Tobacco Field
Slaves toiled endlessly, clearing land, plowing fields, raising livestock, erecting buildings, and planting crops to transform frontier landscapes into lavish plantations.
The enslaved population on Wessyngton Plantation primarily produced tobacco, which was very labor intensive. In 1860, 250,000 pounds of tobacco was produced on Wessyngton making it the largest producer of tobacco in the United States and the second largest in the world.
Tags:African American Plantation Life, African American slavery, black history, Civil War, plantation slavery, Plantation Slaves, Slave Labor, Slave Life, Slavery in America, Tennessee slavery, tobacco plantation, Tobacco Production
Posted in Civil War, Genealogy & DNA, Uncategorized | Comments Closed
Monday, October 5th, 2009

Wessyngton Slave Cabins
Housing for slaves varied from plantation to plantation depending on the owners. Most slave quarters were generally arranged in avenues or streets and located behind the mansion or ‘Big House.’ They were strategically placed to give the owner or overseer a clear view of the slaves, so their activities could be easily monitored.
The slave settlement at Wessyngton Plantation, however, did not fit this pattern. The lack of a clustered settlement pattern at Wessyngton was somewhat unusual during antebellum times. This was primarily due to the hilly topography of the plantation. The scattered pattern gave the slaves at Wessyngton more freedom and made it far more difficult to keep them under constant surveillance.
Typically, slave housing at Wessyngton consisted of hand-hewn one-room log cabins measuring 20 by 20 square feet with brick end chimneys. Some cabins were 18 by 36 square feet. Each cabin had log flooring and a loft, where children slept.
Each cabin housed an average of six individuals. Family sizes varied depending on the number births, deaths and marriages.
Tags:African American Family Life in Slavery, African Slavery, Antebellum Mansion, Antebellum Plantation, Big House, Civil War, Great House, Log Cabin, Log Housing, Overseer, Slave cabins, Slave Family, Slave Houses, Slave Housing, Slave Plantation
Posted in Civil War, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Sunday, September 6th, 2009

List of Men and Boys on Wessyngton Plantation 1856
Plantation owners used records such as slave bills of sales, birth registers, and many other documents to keep an accurate count of their slaves’ births, deaths, and their production on plantations and farms. These documents are invaluable in tracing African American genealogy.
The document above is a list of enslaved African American men and boys on Wessyngton Plantation in 1856 owned by George A. Washington. Slave owners had to pay taxes on their slaves from age twelve to fifty, so the list only identifies those in that age range who were a part of the plantation labor force. Many of the individuals are listed with surnames: Davis, Fairfield, Gardner, Holman, Lewis, Price, Smith, Terry, Vanhook, White and Woodard. The use of these surnames made it possible to locate them and their previous slave owners. Many of them were also found on the 1870 U. S. Census living on or near Wessyngton Plantation.
In 1964, the Washington family deposited all their family papers and plantation records in the Tennessee State Library and Archives in Nashville. Hundreds of these documents shed light on the lives of hundreds of African Americans enslaved there.
Tags:African American Genealogy, African American History, African American Surnames, Black Genealogy, Civil War, Genealogical Research, Naming Patterns, Plantation Life, Plantation Records, Roots, Slave Surnames
Posted in Civil War, Genealogy & DNA, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Tuesday, August 4th, 2009

Letter from Queen Elizabeth
Queen Elizabeth acknowledged the receipt of a signed copy of my book. As is the custom, her lady-in-waiting wrote me. The royal seal indicated that the Queen was at her summer residence, Balmoral Castle in Scotland.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balmoral_Castle– for your info.
Tags:African American History, Balmoral Castle, Buckingham Palace, Civil War, Genealogical Research, President Washington, Queen Elizabeth, Royal Family, Slavery, Tennessee history, Washington family
Posted in Civil War, Current Events, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Monday, May 18th, 2009

Baker at the Hermitage
On May 17th a dedication ceremony was held at The Hermitage, the plantation owned by President Andrew Jackson, in honor of 60 African Americans who had been enslaved on the Ingleside and Cleveland Hall Plantations. Both plantations were owned by nephews of Rachel Jackson and had ties to the enslaved population at The Hermitage.
As reported by the Associated Press, a memorial sculpture of seven oak trees in the shape of the Little Dipper was laid out among a circle of thirty boulders. The piece by Lee Benson is named “Our Peace, Follow the Drinking Gourd.” Slaves fleeing to the North would follow the North Star, one of the stars in the Little Dipper.
Following the ceremony I gave a presentation and did a book signing. It was a very special and meaningful event.
Tags:Andrew Jackson, Civil War, Cleveland Hall, Enslaved Memorial, Hermitage, Ingleside, Rachel Jackson, Tulip Grove
Posted in Book Tour & Reviews, Civil War, Current Events, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research | Comments Closed
Monday, May 18th, 2009
My half-hour television interview with John Seigenthaler Sr, A Word on Words, is available as a free downloadable Podcast.
http://www.wnpt.org/productions/wow/
Mr. Seigenthaler asked me many in-depth thought-provoking questions. At the end, he said, “I learned more from your book than I learned from reading my friend Alex Haley’s book called Roots.” I hope you enjoy the interview. Leave a comment with your reaction.
Tags:Abraham Lincoln, African American History, Black History Month, book review, Civil War, DNA Research, Emancipation, family history, family tree, Genealogy & DNA, George Washington, John F. Baker Jr., John Siegenthaler, plantation slavery, Reconstruction, Roots, Simon & Schuster, Tennessee slavery, Washington family, Wessyngton Plantation, WNPT, Word On Words
Posted in Book Tour & Reviews, Civil War, Current Events, Genealogy & DNA, Interviews, Introduction & Personal, Plantation Life, Research, Videos & Audios | Comments Closed