On July 11th Nashville Public Television aired its documentary Wessyngton Plantation: A Family’s Road to Freedom. The film was inspired by my book The Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation: Stories of My Family’s Journey to Freedom and the Tennessee State Museum exhibition Slaves and Slaveholders of Wessyngton Plantation. The documentary highlighted the life of my great-great-great-grandmother Jenny Blow Washington. Jenny along with her sister Sarah was brought from Sussex County, Virginia to Tennessee in 1802 by Joseph Washington who founded Wessyngton Plantation. Jenny married Godfrey a slave from a neighboring plantation and became the matriarch of one of the largest families on Wessyngton. Godfrey and Jenny later had nine children, including my great-great-grandfather Emanuel Washington (1824-1907). Today there are thousands of their descendants throughout the United States. Click link to view the documentary: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bdce9dud1c0
Posts Tagged ‘Tennessee slavery’
WESSYNGTON PLANTATION: A FAMILY’S ROAD TO FREEDOM
Saturday, July 12th, 2014Slave Bill of Sale Reveals History of 14 Slaves on Wessyngton Plantation
Saturday, June 14th, 2014Slave Bill of Sale from Union Bank of Tennessee to George A. Washington 1842
Among the thousands of documents in the Washington Family Papers housed in the Tennessee State Library and Archives are approximately 50 slave bills of sales. These sales involved 130 enslaved individuals purchased by Joseph Washington and his son George A. Washington from 1801 to 1843. The sales included several nuclear families: mothers and their small children; a family of five brothers; five men from the same plantation of unknown relationships; 29 slaves made up of 7 interrelated families; and one discussed here which includes fourteen slaves.
In June 1842, George A. Washington purchased 14 slaves from the Union Bank of Tennessee. Included in the transaction was William, described as a first-rate blacksmith. He was listed later on Wessyngton documents as Billy “the smith” and became Bill Smith after Emancipation. His wife Sylvia, their sons Tom and John and daughters Mira and Louisa were also listed.
Another family was Dick Scott, his wife Ann and their 2-year old daughter Sarah. Dick and Ann’s son, William Henry Scott, who was born at Wessyngton enlisted with the United States Colored Troops during the Civil War.
Also included in the purchase were Sally, Anderson, Edward, Henton and Aggy. It is not known if they were related; they could have been siblings. Aggy later married Dick Terry who was brought to Wessyngton Plantation 4 years earlier.
The descendants of those African Americans who were purchased in 1842 now number in the thousands.
Know all men by these presents that I Albert K. Wynne of Davidson County, Tennessee as agent and attorney in fact of the President, Directors & Company of the Union Bank of the State of Tennessee duly authorize and appointed for that purpose for and in consideration of the sums of money herein after mentioned to me in hand paid by George A. Washington of the county of Robertson & State aforesaid have bargained sold and delivered and do by these presents bargain sell and deliver unto the said George A. Washington the following described negro slaves to wit: William a man aged about forty years for the sum of eight hundred dollars; Sylvia a woman aged about thirty-six years for the sum of three hundred & fifty dollars; Tom a man aged about fifteen years for the sum of five hundred dollars; Mira a girl aged about thirteen years for the sum of three hundred & fifty dollars; John a boy aged about four years for the sum of two hundred dollars; Louisa a girl aged about fifteen months for the sum of one hundred dollars; Ann a woman aged about twenty-eight years for the sum of four hundred dollars; Dick a man aged about thirty years for the sum of six hundred dollars; Sarah a girl aged about two years for the sum of one hundred dollars; Sally a girl aged about thirteen years for the sum of three hundred dollars; Anderson a boy aged about sixteen years for the sum of five hundred dollars; Edward a boy aged about eleven years for the sum of three hundred dollars; Henton a boy aged about seventeen years for the sum of five hundred and twenty-five dollars; and Aggy a woman aged about eighteen years for the sum of four hundred dollars; being in all fourteen in number and the whole consideration paid being the sum of five thousand four hundred and twenty-five dollars. To have and to hold the said negro slaves and each and every of them unto the said George A. Washington his executors administrators and assigns forever. And the said Albert H. Wynne by virtue of the authority in him vested as aforesaid doth for and on behalf of the said President, Directors & Company and of their successors in office covenant and agree to and with the said George A. Washington his executors administrators and assigns that the said negro slaves and each and every of them are healthy, sound and slaves for life and also that they the said President, Directors & Company have good right and title to sell and dispose of them and further that the said negro slave William is a first-rate blacksmith.
In testimony whereof the said Albert H. Wynn, agent and attorney
RECENTLY DISCOVERED PHOTOGRAPH FROM WESSYNGTON PLANTATION
Friday, November 29th, 2013
In preparation for the Tennessee State Museum exhibit, Slaves and Slaveholders of Wessyngton Plantation, descendants have been asked to locate Wessyngton artifacts, photographs, paintings and other memorabilia. A descendant of the owners of Wessyngton living in Nashville recently discovered this photograph in an album that belonged to his grandmother. The photograph was taken at Wessyngton in 1903, featuring Jenny Washington b. 1830, (wife of Allen Washington), Emanuel Washington 1824-1907 and his sister Susan Washington b. 1821. When the photo was taken there were only five former slaves still at Wessyngton of the senior generation, which also included Henny Washington 1839-1913 and Aggy Washington Terry, b.1824.
Wessyngton Plantation African American Cemetery 1796 to 1928
Thursday, November 29th, 2012
The African American Cemetery on Wessyngton Plantation was founded by Joseph Washington who came to Robertson County, Tennessee from Southampton County, Virginia in 1796. Joseph later returned to Virginia and brought African and African American slaves with him. The cemetery was used by the enslaved African American population of the plantation and their descendants from 1796 to 1928.
In 1995 a memorial monument at the African American Cemetery was erected by Mary Washington Holley, Thomas Blagden and Preston Frazer, direct descendants of Wessyngton’s founder Joseph Washington. It honors those buried there.
In 2012 a beautiful six-foot aluminum fence was erected to enclose and protect the cemetery. The fence adds charm and dignity to the cemetery. Special thanks go to Stanley Frazer Rose, a sixth generation descendant of Joseph Washington, for his generosity in funding this renovation.
The African American cemetery is located some distance from the Wessyngton mansion on a hill overlooking Caleb’s Creek. This is near where Joseph and his slaves first settled in 1796. The cemetery measures approximately 640 square feet and contains an estimated 200 graves. A geophysical survey using ground penetrating radar is planned to determine the actual number of graves in the cemetery. At that time, the original monument will be enlarged to honor all those who were buried in the cemetery. This monument will be funded in part by Mary Hotchkiss Gregg, Robina Gregg O’Rourke, Robert Etheridge Gregg, and Robert Hunnewell Gregg, sixth generation descendants of Joseph Washington.
Based on correspondence and plantation records from the Washington Family Papers collections, death certificates, oral history and eyewitnesses who attended burials at the cemetery, the following persons are known to be buried there:
Sampson Washington 1808 –1836
Caesar Washington 1826-before 1838
Elijah Washington 1823-before 1838
Matt Washington 1777-before 1838
Nicholas Washington 1822-before 1838
Noel Washington 1804-before 1838
Oscar Washington 1825-before1838
Peter Washington 1823-before 1838
Sam Washington 1770-before 1838
Sam Washington 1770-before 1838
Samuel Washington 1770-before 1838
Simon Washington 1783-1835-before 1838
Cherry Washington 1839-1839
Will Washington 1820-1841
Boyd Washington 1840-1846
Mariah Washington 1798-1846
Godfrey Washington 1787-1846-before 1850
Rosetta Washington 1827-1850
Camilla Lewis 1834-1852
Maria Washington 1853-1853
Wendy Washington 1853-1853
Westley Washington 1853-1853
Otho Lewis 1838-1854
Edward Washington 1834-before 1856
Al Washington ?-1838-before1856
Andrew Washington ?-1838-before 1856
Fowler Terry 1815-1838-before 1856
Simon Washington 1815-1838-before 1856
Toby Washington ?-1838-before 1856
Tony White 1820-1838-before 1856
Westley Washington 1822-1838-before 1856
Daniel Washington 1808-1841-before 1856
Wallis Washington 1822-1841-before 1856
Anthony Washington 1823-1843-before 1856
Archer Washington 1824-1843-before1856
Charles Washington 1809-1843-before 1856
George Lewis 1785-1843-before 1856
Jim Washington 1801-1844-before 1856
Aleck Washington 1795-1846-before 1856
Norfleet Washington 1846-before 1856
Tom Washington 1783-1846-before 1856
Gabriel Washington 1819-1850-before 1856
Dempry Washington 1837-1856
Ned Washington 1844-1856
Silvah Washington 1817-1823-before 1860
Charity Washington 1828-before 1860
Martha Ann Washington 1833-before 1860
Martha Washington 1835-before 1860
Sarah Washington 1840-before 1860
Arry Leavell Washington 1805-1841-before 1860
Sally Washington 1816-1829-before 1860
Mira Washington 1829-1842-before 1860
Sylvia Washington 1806-1842-before1860
Bena Washington 1770?-1844-before 1860
Tom Washington 1782-1846-before 1850
Easter Washington 1784-1850-before 1860
Henny Jackson Smith 1790-1850-before 1860
Jenny Washington 1760-1850-before1860
Unknown male 1785-1850-before 1860
Willie Washington 1820-1850-before 1860
Angelina Cheatham Washington 1814-1851-before 1860
Millie Washington 1851-before 1860
Allen Washington 1813-1856-before 1860
Mose Terry 1810-1856-before 1860
Westley Washington 1830-1856-before 1860
Hannah Washington 1780-1801-before 1860
Juda Washington 1775-1801-before 1860
Nanny Washington 1802-1804-before 1860
Rhoda Washington 1814-1819-before 1860
Fanny Washington 1815-1831-before 1860
Peggy Lewis 1795-1843-before 1860
Lettuce Washington 1857-before1860
Green Cheatham 1817-1860
Jack Washington 1849-1860
Marian Lewis ?-1843-1860
Temperance Washington 1795-1861
Amanda Washington 1837-1863
Aaron Gardner 1804-1860-before 1865
Esther Washington 1775-1860-before 1865
Jenny Washington 1785-1860-before 1865
Sarah Washington 1810-before 1865
Jack Washington 1859-1865
Moses Lewis 1857-1866
Vina Washington 1843-1869
America Washington 1815-1870-before 1880
Humphrey Washington 1797-1870-before 1880
Jenny Blow Washington 1792-1870-before 1880
Cornelia Washington 1859-1882
Axum Washington 1808-1880-before 1890
Britain Washington 1800-1880-before 1890
Hannah Washington 1808-1880-before 1890
Prudence Washington 1819-1893
Allen Washington 1825-1890-before 1895
Emanuel Washington 1824-1907
Jenny Washington 1830-1900-before 1910
Winnie Washington Long Biggers 1860-1900-before 1910
Henny Washington 1839-1913
Sarah Washington Cheatham 1810-1914
Hezekiah Tom Washington 1850-1918
Henry Drake 1868-1928
National Black Arts Festival Study Group Walks in Footsteps of Baker’s Ancestors on Wessyngton Plantation
Sunday, June 13th, 2010
In addition to touring the grounds surrounding the Wessyngton mansion, National Black Arts Festival members and guests walked in the footsteps of Baker’s ancestor in the slave cabin area of the plantation. The group went inside a restored slave cabin built ca. 1830. In 1860, there were 274 enslaved African Americans on the plantation, housed in forty log cabins. At the onset of the Civil War, Wessyngton held the largest African American population in the state of Tennessee and was the largest tobacco producer in America.
Author Shows History Begins at Home
Thursday, March 4th, 2010The Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation reviewed in Nashville City Paper by Todd Dills. Click here to see review.
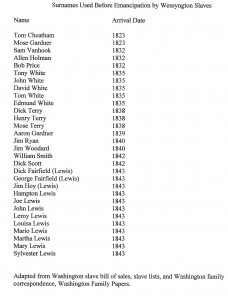
Use of Surnames Among African Americans Before Emanicaption
Tuesday, November 10th, 2009Slaves were usually known by their first names, especially on small farms with few slaves. Plantation owners rarely recorded their slaves with surnames unless they had several individuals with the same first names. For that reason the use of surnames by slaves was far more common on large plantations where more people were likely to have the same given names.
Due to Wessyngton Plantation having such a large enslaved population many African Americans are listed with their previous owners’ surnames as early as the 1820s.
Slave bills of sale and other documents in the Washington Family Papers collection details the origins of many of these African American families.
The list above documents the names African Americans on Wessyngton Plantation who used surnames prior to emancipation and the date of their arrival on the plantation.
Slave Descendant Walks in Ancestors’ Footsteps on Wessyngton Plantation
Monday, November 2nd, 2009In 1991, I had an opportunity that few historians or genealogists ever have; to literally walk in your ancestors’ footsteps. In 1989 I was approached by the president of the Bloomington-Normal black history Project and director of the Midwestern archaeological research Center, about the potential investigations of the salve cabin area on Wessyngton Plantation to get an interpretation of slave life there. Similar digs have been conducted at the Hermitage, Mt. Vernon, and Monticello.
The actual digging at Wessyngton did not start until 1991. The thought of actually walking in my ancestors’ footsteps and holding objects they used in their everyday lives one hundred years earlier was surreal to me. Three sections of the slave cabin area were selected for exploration. One site was where the cabin of my great-great-grandparents Emanuel and Henny Washington once stood.
The dig yielded fragments of pottery and dishes used by my ancestors as well as coins and arrowheads made by Native Americans.
The photograph above shows the site of the archaeological dig on Wessyngton Plantation where my ancestors once lived.